Levels of Learning
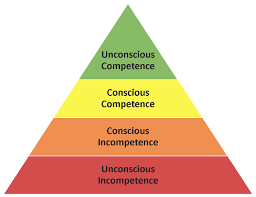
Technically, the term is “Four Stages of Competence” and was originally established in the 70s. The idea is that learners are not aware of how little or much they know. They go through the four (or five) stages listed below, depending on how much they know about a given topic or skill.
In the end, the learner will be able to use the knowledge or skill without having to think about what they’re doing. It is important to keep these stages in mind when developing eLearning because different learners will be at different stages.
Unconscious Incompetence
In this stage, the learner does not have a skill or knowledge set yet. They do not see any reason to learn it because they don’t consider it a need. You don’t know what you don’t know. For example, as a very young child you do not yet realize the usefulness of riding a bike.
As an educator, it is important to work on how to best market learning offerings to those in this stage. They may or may not realize the benefits of your education yet, but the objective is to reveal that there ARE benefits. If you introduce potential learners to your offerings, they may realize that they CAN gain value from those skills and knowledge sets and reach stage two, conscious incompetence.
Conscious Incompetence
By the second stage the learner is aware of the skill that they lack and can understand that there is a deficit. Ignorance is no longer bliss. Ideally, this is who should be signing up for the majority of your online courses. In this stage, the learner wants to learn because they are aware of their lack of knowledge and it makes them uneasy. Selling courses to this demographic should be easiest.
Conscious Competence
The conscious competence stage takes place when a learner has acquired a skill but has not yet mastered it to the point where it comes naturally. Imagine you have learned the steps to riding the bike, but you still need to go through the steps when getting on the bike, or you need training wheels. This is when the learner usually needs testing, instructors, or other tools to hold their hand through it, or even talking themselves through the steps.
At this point the learner uses your online courses to gain fluency in the skills and become an engaged learner who wants to reach the fourth stage. Think of this learner as a student studying for a test. They feel prepared but sometimes still rely on flash cards.
Unconscious Competence
You know the phrase, “It’s like riding a bike. You never forget how to do it.” The fourth stage of learning encompasses just that: you know it so well you don’t even realize you are doing it. The skill is so embedded that the learner doesn’t even need to process what they are doing. Issues can arise when you combine unconscious competence learners with unconscious incompetence learners because neither of them can articulate the skill.
Stage 5 Learner
Some theorists believe there is a fifth stage as well — “conscious competence of unconscious competence.” In this stage the learner is able to relate to learners in stages 1-4 enough to teach them. A stage five learner has reached a point where they can reflect on how they reached their level of mastery. This means that they can empathize with learners in other stages. In NLP this stage is the focus of the Trainer’s Training
When done please take the time to reflect on the lesson and post a comment or question below. What was your reaction to the videos? What insights did you gain? What questions arose for you?
Also, consider responding to the comments of others to start a dialogue.
After you have posted your comment hit the Mark Complete Button and move on to the next lesson.
Responses
You must be logged in to post a comment.

The Four (Five) Stages of Competency each category broken down by its distinction – leading up to stage 5 where Competency is evident for Training the Trainer.