Online MindBridge NLP Coach Certification Training
-
Managers as Coaches
-
1 - Introduction to Professional Life Coaching and NLP8 Topics
-
2 - Fundamentals of Influential Communication5 Topics
-
3 - a. Characteristics of Excellence in Communication2 Topics
-
4 - a. Identifying Thinking Styles1 Topic|1 Quiz
-
4 - b. Rapport
-
5 - a. Values Clarification
-
3 - b. Submodalities
-
7 - a. Power of Questions
-
6 - a. Anchoring Techniques2 Topics
-
7 - Clarifying Communication5 Topics
-
7 - b. Intake- Initial Pre-Coach Session
-
8 - Criteria3 Topics
-
8 - a. Perceptual Flexibility - Perceptual Position Quiz3 Topics
-
8 - b. Well-Formed Outcomes3 Topics
-
9 - 3 NLP Techniques Demonstrations
-
10 - Identifying Mind Maps
-
10- a. Meta Program Psychometric Quizzes
-
10 - b. Key Meta Program Patterns Explained7 Topics
-
10 - c. NLP Coach Session Demonstration
-
10 - d. Evaluation Forms -Outcome Coach Session
-
10 - e. Evaluation Video of NLP Coaching Demonstration
-
11 - NLP Coaching Sessions2 Topics
-
11 - a. Evaluation of Demo - Categories of Experience
-
11 - b. Directionalizing the Session
-
12 - Insights and Just for the fun of it!
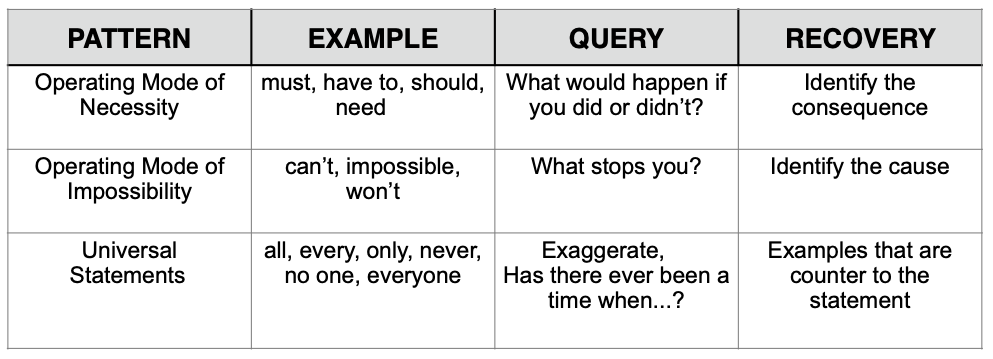
Meta Model Distinctions – Limits of Speaker’s Model – Generalizations
- An Operating Mode of Necessity is a verbal pattern identifying rules or limits to behavior. They are words that require (rule) particular action.
Examples of Operating Mode of Necessity are:
- “You should know this.”
- “People need to act properly.”
- “I have to get this right.”
The Meta Model challenge to this pattern will identify the consequences responsible for the rule or boundary and take the speaker into the future.
2. An Operating Mode of Impossibility is a verbal pattern identifying rules or limits to behavior. They are words that limit or imply no choice.
Examples of Operating Mode of Impossibility are:
- “I can’t learn this.”
- “It’s impossible to change.”
The Meta Model challenge to this pattern will identify the cause of the problem, state symptoms and take the speaker into the past.
3. A Universal Statement is a broad generalization that precludes exceptions or alternative choices.
Examples of Universal Statements are:
- “Everybody knows this.”
- “He is always right.”
- “They never consider my feelings.”
The Meta Model challenge to a Universal Statement will identify examples that are counter to the limiting generalization.
Generalizations Recovery Chart
Responses
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Meta Model Distinctions – Limits of Speakers Model – Generalizations
1) Category is an Operating Mode of Necessity (Operating Modal of Necessity) – identify rules or limits to behavior. They are words that require (rule) particular action.
Example:
“You should know this.” RESPONSE: “What would happen if I didn’t know this?”
“People need to act properly.” RESPONSE: “What would happen if people didn’t act properly?”
“I have to get this right” RESPONSE: “What happens if you do not get this right?”
MM Challenge will identify the consequences. rules or limits to behavior. Words that imply no choice.
2) Operating Model of Impossibility ( Operating Modal of Impossibility) Identifies rules or limits to behaviors words that imply no choice.
Example:
“I can’t learn this.” RESPONSE: “What stops you from learning this?”
“It’s impossible to change.” RESPONSE: “What stops you from changing?”
MM Challenge identify cause or problem, state symptoms and take speaker into the past.
3) Universal Statement – a broad generalization that precludes exceptions or alternative choices.
Example:
“Everybody knows this.” RESPONSE: “EVERYBODY?”
“He is always right.” RESPONSE: “Has there ever been a time when he wasn’t?”
“They never consider my feelings.” RESPONSE: ” NEVER”
The MM Challenge to a general statement will identify examples that are counter to the limiting generalization.