
Gathering specific information will give you the components that make changing or modeling experience possible.
Information gathering is one of the most important parts of NLP. Eventually you get to the point where you simply go on automatic and, gathering lots of information simultaneously, you end up with a deep understanding of how a person does what they do.
Language is comprised of words that are intended to convey a meaning to the listener, and hopefully those meanings align with the intent of the speaker. What makes the difference is how the words are put together to generate meaning . . . this is the form or the context. The words alone are content. Identifying language patterns in form and context allows you to step more completely into another person’s world model. Through precise and gentle questions you can specify, at a level which most anyone could share, another’s experience and behavior.
Information about the desired state will let you know whether it is a worthwhile outcome and whether there is a sufficient representation that will allow your client to recognize their outcome if they get it. Before you can structure language precisely, you must first understand precisely what outcomes you want. If you don’t know where you’re going, then a map is of little value. So the first criterion is KNOW WHAT OUTCOME YOU WANT.
The second step is to understand what specific words will do. It is the result they produce that allows you to structure your language so that your communication will produce the outcome you want. One way we gather information is through the questioning process; it is useful to know what ‘question’ words will elicit:
To improve your ability to communicate, a key factor is listening and then seeking to clarify what the other person means. The Meta Model will help you obtain information from the speaker rather than assigning your own subjective meaning based on your experience.
Meta Model queries or challenges enable you to gather high-quality information by preventing ‘mind reading’, and allowing you to quickly and precisely check out assumptions.
We understand information by deleting some of it, generalizing some of it and distorting some of it. These are universal human processes and very useful.
They are, from most to least important: Distortion, Generalization and Deletions. Each person’s combination and prevalence of these patterns is a unique linguistic description of how they hold their world model intact.
The Meta Model is a set of language categories and questions that:
- Allow the listener to stay in external sensory experience when someone is talking.
- Linguistically describe the speaker’s model of the world.
- Reconnects language to experience.
- Assists the listener in changing the speaker’s world model when appropriate.
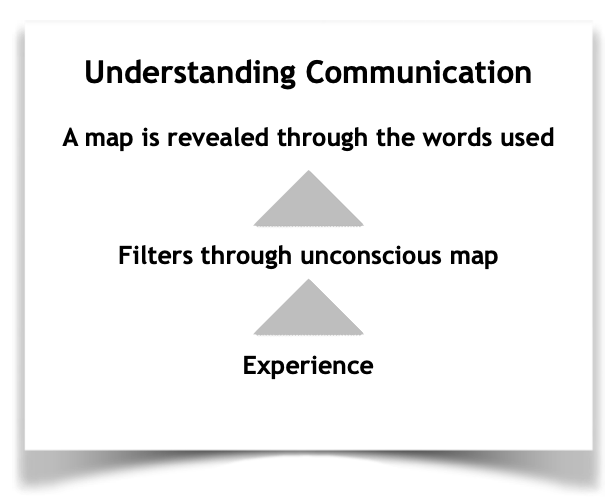
When we communicate our ideas, there is a triple filtering that happens. Our communication must pass through and we must deal with:
- How we individually create our model of the world (map) – Experience
- How we choose to represent that model, i.e., which words we use – Filters
- How the listener will construe our communication according to his/her map – Words
The ability to use language with precision is essential to any professional communicator.
Language can never do justice to the speed, variety and sensitivity of our thinking. It can only be an approximation. When human beings create their linguistic model (map) of the world, they necessarily select and represent certain portions of their experience and fail to represent others.
A full linguistic representation of experience — the Deep Structure — will differ from the reduced version communicated — the Surface Structure. While the reduction may be useful, it may also impoverish the map in such a way that it creates problems for the person. The technique of recovering the full linguistic representation — the Deep Structure — with the Surface Structure is known (in NLP) as the Meta Model.
The Meta-Model is designed to teach the listener how to hear and respond to the form of the speaker’s communication in order to recognize deletions, generalizations, and distortions, and to prevent mind reading. It is a series of linguistic skills designed to reconnect language to experience.
Responses
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Clarifying Communications is by Gathering information which makes changing and the modeling experience possible.
Context is how words are put together; content are the words alone.
Language patterns are in the form and context allowing the capability to step into another person’s world model.
In NLP we begin with Information Gathering – the Desired State is it a worthwhile outcome. Going through the process the client recognizes whether or not the outcome is the outcome they want – is it well formed outcome – does it meet criteria?
Improving the listeners (coach) ability to communicate by clarifying the clients meaning, the Meta Model is used to query or challenge the client’s communication and enables the coach to gather higher quality information without mind reading. Understanding the meaning of the communication when there exists distortions, generalizations or deletions.