MindBridge NLP Coach Certification Training
-
1 - Introduction to Professional Life Coaching and NLP8 Topics
-
Managers as Coaches
-
2 - Fundamentals of Influential Communication5 Topics
-
3 - a. Characteristics of Excellence in Communication2 Topics
-
3 - b. Submodalities
-
4 - a. Identifying Thinking Styles1 Topic|1 Quiz
-
4 - b. Rapport
-
5 - a. Values Clarification
-
6 - a. Anchoring Techniques2 Topics
-
7 - Clarifying Communication5 Topics
-
7 - a. Power of Questions
-
7 - b. Intake- Initial Pre-Coach Session
-
8 - Criteria3 Topics
-
8 - a. Perceptual Flexibility - Perceptual Position Quiz3 Topics
-
8 - b. Well-Formed Outcomes3 Topics
-
9 - 3 NLP Techniques Demonstrations
-
10 - Identifying Mind Maps
-
10- a. Meta Program Psychometric Quizzes
-
10 - b. Key Meta Program Patterns Explained7 Topics
-
10 - c. NLP Coach Session Demonstration
-
10 - d. Evaluation Forms -Outcome Coach Session
-
10 - e. Evaluation Video of NLP Coaching Demonstration
-
11 - NLP Coaching Sessions2 Topics
-
11 - a. Evaluation of Demo - Categories of Experience
-
11 - b. Directionalizing the Session
-
12 - Insights and Just for the fun of it!
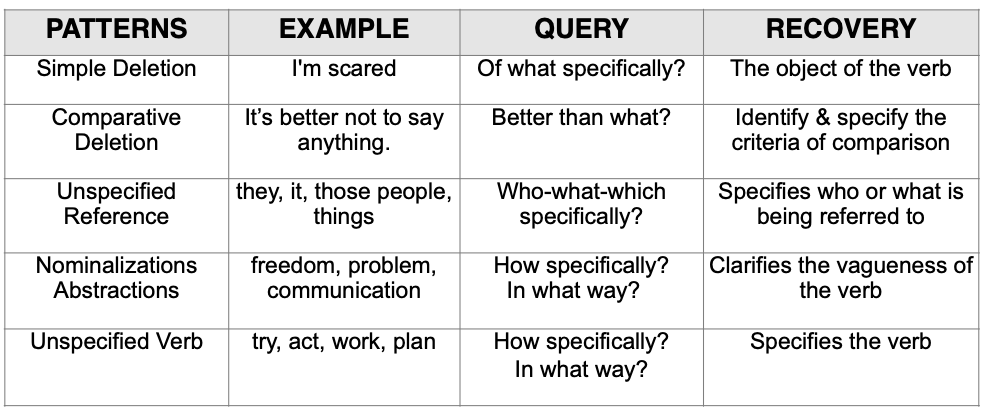
Meta Model Distinctions – Gathering Information – Deletions
- A Simple Deletion is a statement with missing or deficient information.
Examples of Simple Deletions are:
- “I’m confused.”
- “I am uncomfortable.”
- “She’s unhappy.”
The Meta Model challenge to a Simple Deletion will recover the deleted information.
Ask “What are you ______ about?”
2. A Comparative Deletion is a verbal pattern where the standard of evaluation is missing in the surface structure.
Examples of Comparative Deletions are:
- “She’s a better person.”
- “It’s best to stay.”
- “This means more than you think.”
The Meta Model challenge to a Comparative Deletion will recover the comparator.
Identify the comparator and add – “than what?”
3. An Unspecified Reference is a verbal pattern where the noun or object is not specified (unidentified pronoun).
Examples of Unspecified Reference are:
- “People just don’t learn.”
- “They don’t listen to me.”
- “That doesn’t matter.”
The Meta Model challenge to an Unspecified Reference will recover what or who the referent is.
Ask: “Who or what specifically?”
4. An Unspecified Verb is a verbal pattern in which the verbs delete specifics about how, when and where, leaving the details of the action or relationship undefined.
Examples of Unspecified Verbs are:
- “I have difficulty with communicating my feelings.”
- “She rejects me.”
- “They really hurt me.”
- “I care about him.”
The Meta Model challenge to an Unspecified Verb will reconnect the speaker more completely to their experience by specifying the verb.
Ask: “How exactly?” or “Can you explain how specifically?”
5. An Abstraction (Nominalization) is a word that has been transformed from a process (verb) into a thing or event (noun), thus obscuring the process or action.
Examples of Abstractions are:
- “I regret my decision.”
- “Pay attention.”
- “We have to improve our communication.”
- “Our relationship is not working.”
The Meta Model challenge to an Abstraction will convert the event/thing back to a process, which will recover deletions and referential index.
Restate the abstraction in a question as a verb.
Deletions Recovery Chart
Responses
You must be logged in to post a comment.

The Meta Modal of Distinctions – Gathering Information
1) Deletions fall into 5 Categories:
Simple Deletion is a statement with missing or deficient information:
Example
I’m confused Query: “What are you confused about?”
I’m uncomfortable Query: “What are you uncomfortable about?”
She’s unhappy Query: “What is she unhappy about?”
The Meta Model Challenge will recover the deleted information by ASKING:
“What are you ________ about?”
2) A comparative deletion is where the standard of evaluating is missing the structure:
Example:
She’s a better person Query: ” She is a better person than what?”
It’s best to stay Query: ” It is best to stay than what?”
This means more than you think Query: This means more than you think than what?”
Identify the comparative and the ASK: “Than What?”
3) Unspecified Reference where the noun or object is not specified (unidentified pronoun)
Example:
People just don’t leave Query: “Who doesn’t just leave?”
They don’t listen to me Query: “Who doesn’t listen to you?”
That doesn’t matter Query: What doesn’t matter?”
ASK: “Who or what specifically?”
4) Unspecified Verb is when the verb deletes specifics about How, When or Where leaving the details about the action or relationship undefined.
Example:
I have difficulty communicating my feelings. Query: “Can you explain specifically?”
She rejects me. Query: How exactly does she reject you?”
They really hurt me. Query: “Can you explain specifically who hurt you and how they hurt you?”
I care about him. Query: “How exactly do you care about him?”
The Meta Modal challenge will reconnect the speaker more completely with their experience by specifying the verb.
ASK:
“How Exactly?”
“Can you explain specifically?”
5) The Meta Modal challenge for Abstraction will convert the event or thing back to process which will recover deletions and referential index.
Restate the Abstraction in a question as a verb.